Surgical Spotlight: Laparoscopic Hysterectomy
![]() Theator
on
April 17, 2024
Theator
on
April 17, 2024
Laparoscopic Hysterectomy Insights
Laparoscopic hysterectomy is performed for a variety of indications, the most common of which is symptomatic uterine fibroids. In just over two decades, hysterectomies in the US went from being performed via an open abdominal approach in 70% of cases to being performed laparoscopically 70% of the time.
The laparoscopic approach to hysterectomy offers a number of advantages over open abdominal hysterectomy, including reductions in:
- Recovery time
- Pain
- Blood loss
- Costs
However, like all surgical procedures, laparoscopic hysterectomy has a risk of complications including:
- Urinary tract injury
- Bowel injury
- Vascular injury
- Bleeding
Readmission within 30 days following laparoscopic hysterectomy occurs in 2.6% of patients, with most of these occurring within the first 15 postoperative days. Surgical site infection (28.3%) is the most common reason for readmission. Notably, 51.9% of complications following laparoscopic hysterectomy are related to infections, surgical injuries, and wound complications, which are all potentially preventable outcomes.
These complications can affect patients both physically and emotionally, as well as increase the cost of care.
For more laparoscopic hysterectomy insights, download our procedure spotlight report.
Surgical Practices in Laparoscopic Hysterectomy
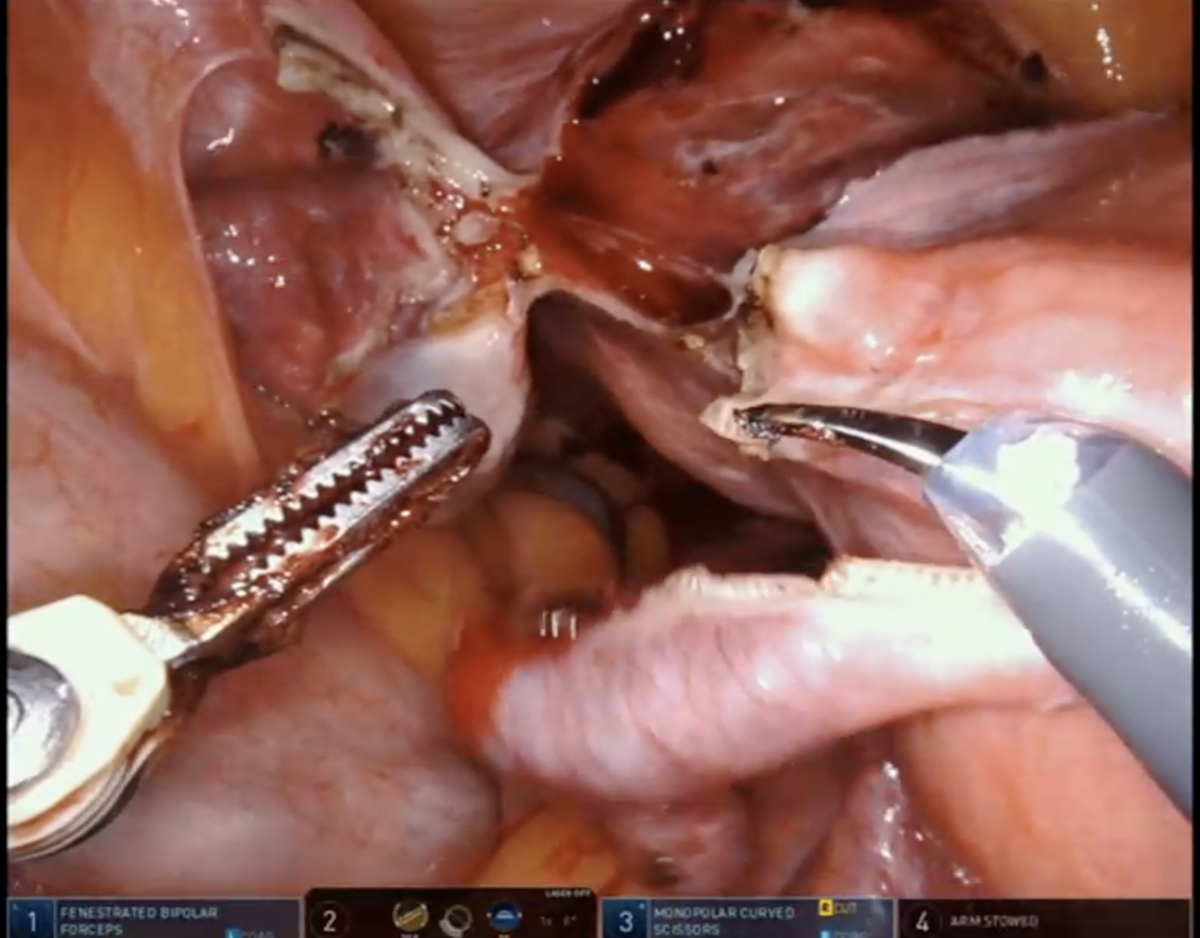
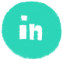
Identification of critical anatomic landmarks is an essential step in preventing surgical complications associated with laparoscopic hysterectomy. For example, identification of the bilateral ureters can prevent injury to these structures.
However, this step isn’t universally performed by all surgeons, and rates of bilateral ureter identification vary by institution. Theator’s Surgical Intelligence database has compiled more than 1150 laparoscopic hysterectomies to date from 9 different health systems, and we’ve found rates as low as 37% and as high as 72% for identification of both ureters at different institutions.
This is just one metric that Theator’s Surgical Intelligence Platform recognizes, analyzes, and connects to health system outcomes so hospital administrators and surgeons can take a data-driven approach to improving the quality of surgical care.
Curious to know what other insights we’ve seen in our database of laparoscopic hysterectomies? Download the full report here