The future of AI-assisted quality improvement
In the matter of a few years, artificial intelligence (AI) has gone from being a topic discussed only by select innovators in the healthcare industry to one of widespread interest and endless discussion. In fact, one study found that the number of publications about AI doubled in the medical literature between 2014 and 2018.
However, it’s always important to remember that quantity does not equal quality. In other words, AI tools are only worthwhile in healthcare if they improve patient outcomes. So what currently available AI technologies improve quality and safety of care? And what does the future of AI-assisted quality improvement look like? Let’s dive in!
Predictive Analytics
While patient safety techniques have traditionally focused on identifying events and near misses after the fact and working to prevent future repeat occurrences, the introduction of AI-powered predict ive analytics flips this concept on its side by allowing identification of potential patient safety issues before they happen.
One example of this is an AI tool used at NYU’s Langone Medical Center to predict hospital readmission rates, a vital patient safety and care quality measure. This technology is able to predict 80% of readmissions and performs 5% better than standard computer tools at calculating readmission risk.
In the surgical realm, predictive analytic tools can improve patient outcomes by triaging surgical patients to the most appropriate postoperative location more reliably than traditional methods*. This can lead to significant improvements in patient safety, as patient undertriaging to a surgical floor instead of an ICU is associated with a longer length of stay and higher mortality rate, among other poor outcomes.
Clinical Decision Support
AI technologies have the power to offer clinical decision support in a manner not previously possible: at the time of decision making, using personalized and up-to-date patient data. Furthermore, AI tools that support clinical decision making have expanded in availability from a few select specialties to nearly all fields of medicine.
Radiology was an easy early target for AI technologies given the technological nature of the field. And while it’s unlikely that AI will ever replace radiologists, use of AI-powered diagnostic tools to augment radiologist readings has been associated with reduced diagnostic errors, with one study showing a 19% reduction of this metric. This not only improves quality by increasing diagnostic accuracy, it also saves money by reducing the cost of unnecessary tests.
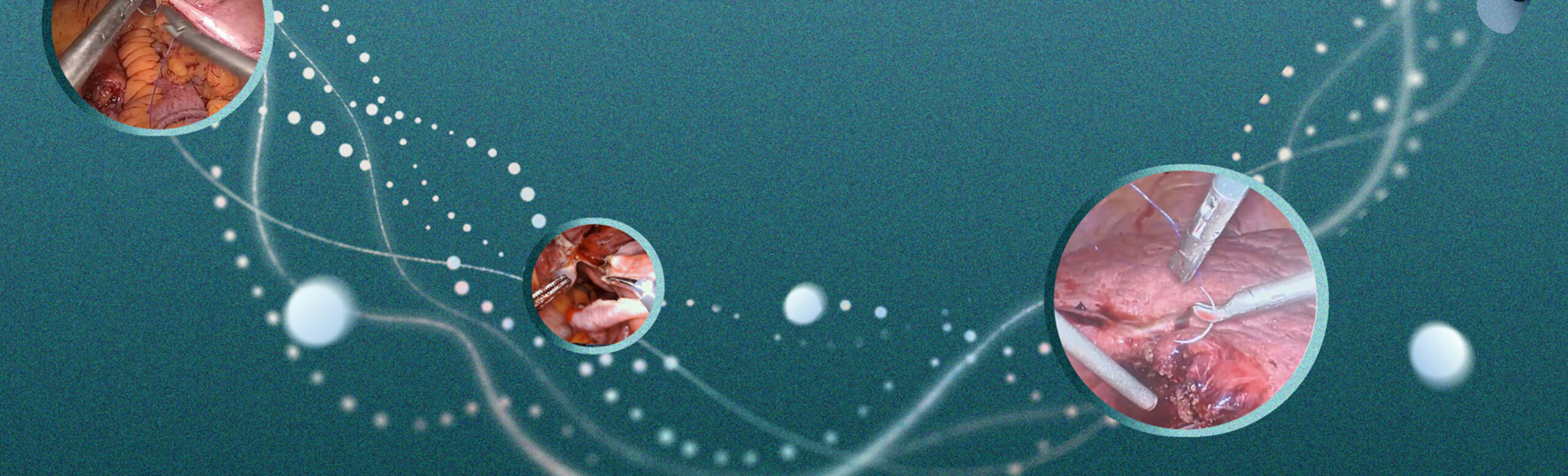
In surgical care, AI tools that offer decision support using real time intraoperative data can improve patient safety by assisting with the identification of critical landmarks for injury prevention. One study evaluating the use of AI in detecting the Critical View of Safety in laparoscopic cholecystectomy found this method to have an 84% accuracy rate. Similar intraoperative AI-guided landmark identification was evaluated during endoscopic hysterectomy and also associated with improved safety awareness and reduced intraoperative complications.
Medical Education
Creating a safe environment for trainees to gain necessary skills and knowledge for practicing medicine in the real world is an area where many have tried to innovate over the years. From simulation labs with mannequins to online fictional patient case scenarios, computer-assisted technology has undoubtedly enhanced the ability of students and residents to learn without putting patients in danger.
AI tools take this concept to the next level by providing guidance and feedback using real patient data, rather than simulations, for enhanced learning. For example, AI virtual patient tools analyze large data sets from actual patients to create true-to-real-life cases for medical students to work through. This not only improves the quality of their training, it also saves valuable time previously spent manually generating such mock cases.
For surgical trainees, harnessing intraoperative recordings and pairing them with AI technology offers a new method of learning and feedback on surgical performance. Identifying critical procedural elements and decision points using AI allows surgical residents to learn from the cases they perform after the fact and use this information to improve the quality of their technique and decision making for future cases.
Improving Quality and Safety Into the Future
The promise of AI for improving healthcare quality and safety lies in its ability to operate in real time, using current patient data to provide assistance and support. This greatly contrasts with traditional models of quality and safety improvement that rely on manual reporting of data with analysis after events have already occurred. Therefore, AI has the power to improve patient care and outcomes in real time, rather than simply using past data to prevent future mistakes.
* Loftus TJ, Ruppert MM, Ozrazgat-Baslanti T, et al. Association of Postoperative Undertriage to Hospital Wards With Mortality and Morbidity. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4(11):e2131669. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.31669
I. Levin, Y. Gil, A. Cohen, 7722 Improved Safety Awareness and Intraoperative Complication Reduction after Implementation of Artificial Intelligence in Hysterectomies, Journal of Minimally Invasive Gynecology, Volume 29, Issue 11, Supplement, 2022, Page S101,ISSN 1553-4650, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmig.2022.09.325.